Anti-Human CD14, mFluor 540 (Clone: 61D3)检测试剂
¥2,576.00
- 分子靶点:CD14
- 种属:人 (Human)
- 标记:mFlour 540
- 亚型:Mouse IgG1, κ
- 克隆号:61D3
在售SKU, F1101408, 70-F1101408-25, 70-F1101408-100
描述
| 商品名 |
Anti-Human CD14, mFluor 540 (Clone: 61D3) 检测试剂 |
|---|---|
| 靶点 | |
| 标记 |
mFlour 540 |
| 仪器 |
适用405nm激光器的流式细胞仪 |
| 亚型 |
Mouse IgG1, κ |
| 克隆号 |
61D3 |
| 推荐应用 |
流式检测 |
| 用量 |
5 μL /Test |
| 纯化 |
亲和层析 |
| 储存液 |
含 0.2% BSA 和 0.2% proclin 950 的磷酸盐缓冲液(pH7.2) |
| 保存条件 |
2 - 8℃避光,切勿冻存 |
结果示例
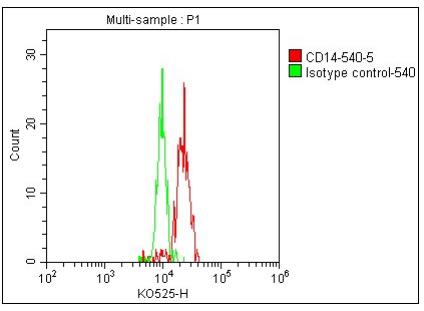
图 - 人外周血进行染色,绿色线为为Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype control, mFluor 540的结果,红色线为Anti-Human CD14, mFluor 540的结果。以单核细胞设门进行分析。
分子信息
CD14 分子靶点信息概述
- 分子名:CD14, CD14 molecule
- 基因家族:CD molecules; Scavenger receptors
- 全称:CD14 antigen
CD14 分子靶点综述
CD14是一种糖磷脂酰肌醇相关的膜蛋白,参与内毒素结合和识别凋亡细胞。CD14抗体可用于研究单核细胞,树突状细胞,组织细胞,肝脏窦状小管中的枯否细胞等。CD14与S100,CD68用于研究组织细胞增多的淋巴结增生性疾病。在单核细胞白血病和组织细胞增生淋巴瘤中肿瘤细胞呈CD14阳性。CD14抗体可以作为弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤以及脾边缘区淋巴瘤的参考依据,其它B细胞淋巴瘤除外。
人 Human CD14 分子靶点信息
- 分子名:CD14, CD14 molecule
- 别称:
- cd14 antigen
- monocyte differentiation antigen CD14
- myeloid cell-specific leucine-rich glycoprotein
- 基因序列:NCBI_Gene: 929
- 蛋白序列:UniProtKB: P08571
人 Human CD14靶点分子功能(预测)
Enables lipopeptide binding activity; lipopolysaccharide binding activity; and lipoteichoic acid binding activity. Involved in cellular response to bacterial lipopeptide; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling; and positive regulation of interleukin-8 production. Acts upstream of or within cellular response to lipopolysaccharide; cellular response to lipoteichoic acid; and positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production. Located in Golgi apparatus and membrane raft. Is anchored component of external side of plasma membrane. Part of lipopolysaccharide receptor complex. Implicated in several diseases, including IgA glomerulonephritis; artery disease (multiple); celiac disease; cystic fibrosis; and pulmonary tuberculosis. Biomarker of several diseases, including biliary atresia; cystic fibrosis; lung disease (multiple); perinatal necrotizing enterocolitis; and polycystic kidney disease (multiple).








官网800x600.jpg)